Benefits of RFID technology
In the industry of production and sale of fur products: for the mandatory marking of fur coats and fur products with a control identification mark.
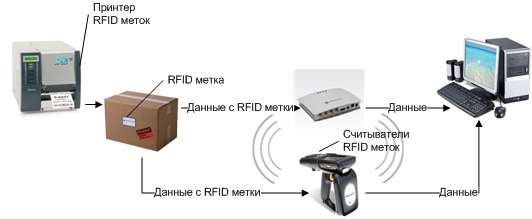
In warehouse and logistics complexes: to track the movement of goods, increase the speed of acceptance and shipment, reduce the influence of the human factor.
In production: to control personnel and transport, ensure safety and prevent emergency situations, account for raw materials. In access control systems and payment systems: for the implementation of contactless automatic access, payment for services using terminals.
- access control applications;
- applications for monitoring and recording working hours;
- vehicle identification;
- production automation;
- warehouse processing automation.
Label and reader orientation independence
Speed and accuracy of identification
Ability to work through materials that transmit radio waves, no need for line of sight
Ability to read the label from a moving object
Ability to store additional information on the tag and rewrite it
The difficulty of counterfeiting RFID tags
Simultaneous reading of several labels (with anti-collision function)
Environmental resistance, long service life
RFID technology is already actively used in manufacturing and trade (to account for goods in warehouses, for example). Using RFID tags, you can track and mark goods, get information about what is inside closed boxes or containers.
In libraries, the radio signal helps to quickly find books, identify users, and make inventory faster.
RFID is most often used for:
- creation of transport maps (subway entrance, public transport);
- remote control of access to the transport fleet;
- executing commands and launching applications on a smartphone;
- to identify people, protect the car from theft;
- identification of plant and machine operators.
Interested in the development of RFID and in the transport sector. For example, special vehicles are already equipped with RFID tags so that they can be easily identified and passed at traffic lights.
In agriculture, using a built-in microchip with a long range, animal identification is carried out to track what is happening with trees and plants.
The use of tags implanted in a person’s hand or in the form of RFID bracelets is not only being discussed, but is already being tested. So far, such tools are used mainly for opening and closing automatic doors. In the future, it will be possible to record a patient’s card with important data (about blood type, allergies, etc.) on the tag.
RFID technologies that capture the radio signal are also used as an electronic passport, for example, in Malaysia. To protect against forgery, a metal anti-skimming device is built into e-passports. Scanning is possible only when the passport is opened. It is impossible to read information in a closed form.
Memory capacity of RFID tags
In general, the memory capacity of RFID tags can vary from 1 bit to hundreds of kilobits. Not always a large amount of memory is an absolute advantage of a radio tag. In general, the expediency of using a label with a particular memory depends on the tasks for which it is used.
So, to implement an RFID solution for the inventory of fixed assets (OS) of a separate enterprise, it is enough to use RFID tags, each of which will contain only a unique number of a particular asset, and all other relevant information, for example, about the location of an object, can be tied to an individual number in a single enterprise database.

Depending on what operations can be performed on the memory of RFID tags, their different types are distinguished:
- Read-Only (RO) RFID tags, read-only;
- Write Once Read Many (WORM) RFID tags for write once and read many times;
- Read-Write (RW) RFID tags that allow data to be overwritten.
Different types of tags have their disadvantages and their advantages. In particular, the first type of tags is more “trivial”, but at the same time more secure, since it excludes the intentional overwriting of radio tags in order to falsify data or fake it. In contrast, RW-type RFID tags can be used for more complex production tasks, but can be deliberately overwritten.
How does RFID work?
The abbreviation RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification. The identification system consists of a reader (reader or reader) and an RFID tag.
How the device works:
- information is written to the microchip of the tag;
- tag antenna receives signal from scanner antenna;
- using the energy of its internal source or the energy of the scanner field, the tag sends the radio signal back;
- the scanner reads the tag’s message and interprets it.
The memory of the tags contains an identification code, as well as a chip on which data and antennas are written for their transmission and receipt of new ones. When the tag enters the registration area, this information is received by the reader.
The process starts if the average distance is no more than 0.05 – 8 meters. There are also RFID long-range identification chips that catch a signal at a distance of 5 to 300 meters. They are mainly used for industrial purposes.
The technology is based on the interaction of an RFID tag (RFID tag) and an RFID reader (RFID reader). R FID tag is a miniature chip that stores a unique tag number and information and has the ability to transmit data to an RFID reader. As soon as the RFID tag enters the range of the RFID reader, the reader records the fact of data transfer, reads the information from the tag and transfers it to the accounting system, which analyzes the data according to predefined algorithms.
At the same time, there can be a distance of up to 300 meters between the RFID tag and the RFID reader (systems operating at a distance of 5 to 300 meters are classified as long-range identification systems, from 20 cm to 5 m – medium-range identification, up to 20 cm – short-range systems identification).
Types of RFID tags by information transfer method
From the point of view of the presence / absence of the ability to independently transmit information, RFID tags are divided into passive, active and so-called semi-active.
Passive RFID tags do not have their own power supply and use the energy of electromagnetic waves emitted by the reader to transfer information back to the reader. Passive tags are the most popular at the moment, which is largely due to their low cost due to the lack of a separate battery.
Active RFID tags contain their own battery and can transmit data on their own, i.e. do not require the reader to supply them with power. The presence of its own battery provides certain advantages for these RFID tags, in particular, the ability to work with greater accuracy and over a greater distance.
Semi-active RFID tags are “mixed-type” tags, using part of their own battery power and part of the electromagnetic field generated by the RFID reader.
RFID Tag Enclosures
RFID tags come in a variety of form factors, from self-adhesive RFID barcode-like labels to highly durable tags built into special metal cases that can withstand extreme temperatures (up to 300 degrees Celsius) and harsh hydrogen sulfide environments. The latter types of tags are also called “body tags”.
The expediency of using certain RFID tags is determined by the characteristics of specific business applications. So, tags, which are RFID labels, can be used to mark clothing tags. To control oil pipes that exist in particularly harsh environments under the influence of high temperature and pressure, only the most durable housing RFID tags can be used.
It should be noted that body radio tags can be used not only to protect an object from harsh environments, but also to attach them to metal surfaces that absorb radio signals and prevent reading. In this case, the housing, in particular, plastic, will allow the antenna enclosed in it to be moved away from the metal at such a distance that would allow reading data from the tag without interruption. Such RFID tags can be attached, for example, to system units in offices to conduct an RFID inventory of property (OS) of an enterprise.
RFID key, access control system
If you do not know how to use RFID equipment, then you can pay attention to the RFID key to control doors, intercom, elevator, barrier, as well as access to VIP apartments.

The signal can be transmitted over a distance of 15 centimeters.
The key is convenient to carry in your pocket or purse and quickly open doors or gates.
The access control system will track the movements of the owner of the key, fix the date of his visit, time. Such a device can always be reprogrammed in accordance with new security requirements.
The control system can be integrated into other systems, creating a full-fledged complex for guarding the entrance to a building or apartment (with connection of cameras, satellite communications).
Thanks to such a well-thought-out system, people are identified and protected from illegal entry and terrorist attacks. R PID-lock can be installed even by yourself. This will require an electromagnetic lock with a controller that will read the tag.
Electric or other types of lock can be connected to stand-alone access control systems. They are computer independent and work with RS485, Ethernet, WiFi, GPRS interface.
- RFID Reader;
- RFID Tag;
- Software.

The reader is engaged in the generation and propagation of electromagnetic waves in the surrounding space. This signal is received by the RFID tag, which creates a feedback signal that is picked up by the antenna of the reader, then the received information is decoded and processed by the electronic unit.
RFID tags: classification
Power Supply
The main classification of RFID tags used is based on the power source – according to it, tags are divided into passive, active and semi-passive.
Passive RFID tags do not have their own power supply and use the energy of the reader’s field to operate. Depending on the architecture of the RFID tag and the type of reader, passive tags work only at a short distance – up to 8 meters, but at the same time they are compact and affordable.
It is passive low-frequency RFID tags that we most often see on goods in stores – representatives of the world’s leading retail chains are working to increase the compactness of tags and reduce their cost.
Active RFID tags are equipped with their own power supply, so they can get additional functions, work at a greater distance and are less demanding on the reader. Their disadvantages, in comparison with passive tags, include their large size and limited operating time of the power source (although today we are talking about a battery life of up to 10 years), but they are indispensable where a large operating radius is needed (up to 300 meters).

Active RFID tags are rightfully considered more reliable, they can transmit a signal even through water or metal, and they can also be equipped with built-in sensors to assess temperature, humidity, light levels and other environmental parameters. Thus, RFID tags can help track, for example, compliance with the storage conditions for certain categories of goods.
Semi-passive RFID tags work on the same principle as passive tags, but have a battery to power the chip. We can say that such a solution is a compromise in terms of cost, size and characteristics of RFID tags.
Performance
By design, RFID tags can be plastic cards, key fobs, body tags, as well as self-adhesive labels made of paper or thermoplastic. There is also an “invisible” label format, which is actually sewn into the product packaging directly at the production stage.
Memory type
According to the type of memory, RFID tags are divided into those intended only for identification (RO, Read Only), designed to read a block of information (WORM, Write Once Read Many) and rewritable (RW, Read and Write).
RO RFID tags are used exclusively for identification – the unique identifier data is recorded during the manufacture of the tag, so it is almost impossible to copy it and fake the tag.
WORM RFID tags allow you to record any data once, which can later be read and used many times. This allows the user, upon receipt, to supplement the tag with their own information, which will then be used when reading.
RW RFID tags contain a memory block that allows you to repeatedly write and read information. The ID of the RFID tag remains unchanged.
Operating frequency
The classification of RFID tags by operating frequency is as follows:
- LF band marks (125-134 kHz)
They are characterized by affordable prices and certain physical characteristics that allow the use of such RFID tags for animal microchip. These are usually passive systems that operate only over short distances.
- HF band markers (13.56 MHz)

RFID tags of this frequency are mainly used for personal identification, in payment systems, for solving simple business tasks (for example, for identifying products in a warehouse). Most RFID systems operating at 13.56 MHz operate in accordance with the ISO 14443 (A/B) standard, which is the standard used by, for example, the Paris public transport fare system.
The disadvantages of RFID systems of the described range include the lack of a decent level of security, as well as possible problems with reading at a long distance, in high humidity conditions, through metal conductors.
- UHF band markers (860-960 MHz)
Designed specifically to work with goods in warehouses and logistics systems, RFID tags in this range initially did not have their own unique identifier. It was assumed that the EPC number of the product would be used as it, but this would not allow controlling the authenticity of the tag, so the development of systems based on the UHF band made it possible to improve the system.
At the same time, the features of RFID tags of this range include high range and speed of operation and the presence of anti-collision mechanisms. Today, the cost of RFID tags in the UHF range is minimal, but the price of other equipment for working in the designated range is quite high.
Near field tags can be classified as a separate category of UHF RFID tags. Using the magnetic field of the antenna, they are technically not radio tags and can be read in high humidity and in the presence of metal. Massive use of near-field labels is expected, for example, in the work with pharmaceutical products that need to be authenticated and accounted for.
UHF tags
| Angstrem Tags | Mikron (HF) and (NFC) Tags |
| CMRFID Tags | Mikron Tags (UHF) |
| Angstrem Tags | Alien Technology Tags |
| TENFID Tags | TRACE-Tech Id Solutions Tags |
| Omni-ID Tags | Motorola Tags |
| Xerafy Tags | Confidex tags |
| UPM Raflatac tags | Boingtech Tags |
Varieties of RFID tags
Electronic tags are active and passive. Active identifiers are supplied with their own power supply, the reading range of such devices does not depend on the energy of the reader. Passive tags do not have their own power source, therefore they are powered by the energy of an electromagnetic signal that is distributed by the reader. The identification range of these tags directly depends on the energy emitted by the reader.
Each of these types of devices has its own advantages and disadvantages. Passive tags are good for their long service life, as well as low cost compared to their active counterpart. In addition, passive identification devices do not require battery replacement. The disadvantage of the device is the need to use more powerful readers.
Active identification devices are characterized by a high range of reading information, unlike passive tags, as well as the ability to recognize and read data when the electronic tag moves at high speed relative to the reader. The disadvantage of active tags is the high price and bulkiness.
Types of RFID identifiers depending on the operating frequency:
- (HF) High frequency RFID tags operating at 13.56 MHz;
- (UHF) Ultra-high frequency RFID tags operating in the frequency range of 860-960 MHz. This range is used in Russia, in Europe RFID tags operate in the range of 863-868 MHz.
Methods for writing information to an identifier (tag):
- ReadOnly devices – identifiers to which information can be written only once, further change or deletion of information is impossible;
- WORM-devices – RFID tags that allow you to write once and read data multiple times. Initially, no information is stored in the device’s memory, all the necessary data is entered by the user, but after recording, it is impossible to overwrite or delete the information;
- R/W devices are identifiers that allow you to repeatedly read and write information. This is the most progressive group of devices, since such tags allow you to overwrite and delete unnecessary information.
RFID technology is widely used in manufacturing, retail, access management and control systems, document forgery protection systems and other fields. It saves time and minimizes the use of manual labor.
Features
Despite the rather high cost of using RFID systems, their implementation is advisable wherever a high level of security and rapid identification of objects are important. In this case, special attention should be paid to the choice of a specific solution, which will depend on many factors:
- Distance between RFID tags and readers
- Presence of shielding surfaces (e.g. metal)
- Need to read data from multiple tags simultaneously (collision protection)
- The need for secure execution of labels, hidden placement of labels
- High requirements for tag security
- Data storage and overwriting
- Ease of integration with your infrastructure
Durability of RFID tags
It is clear from the previous section that RFID tags are particularly durable. This applies not only to body radio tags, but also to self-adhesive RFID labels like a barcode. The durability of RFID tags can be an important benefit in a range of business applications. In particular, when marking the OS of an enterprise with RFID tags, there is no need for their (OS) re-labeling, which occurs when using a barcode that fades over time and needs to be replaced.
Vendors
Tendo offers passive RFID tags from well-established American and European IT manufacturers – Alien Technology, Angstrem, Mikron, Confidex, Omni-ID, UPM Raflatac. R FID tags of these vendors have two main versions – self-adhesive labels and RFID tags in plastic cases.
For detailed information, you can also contact our managers – we will help you make the right choice and select the tags that are best suited for your RFID solution.
How are RFID tags arranged?
The tag consists of an antenna that can receive and transmit a signal from a chip (a device for signal processing and information storage). Using power from its internal source or from power harvested from the scanner’s electromagnetic field, the RFID tag sends a radio signal back.
The reader recognizes the tag by reading the code from it, decrypting it and sending the information. If a scanner, such as a smartphone, is in the tag’s coverage area, it is activated and transmits a signal at a speed of up to 424 kbps.
The amount of information stored in an RFID chip can vary. Up to 1024 bytes of information up to 8 KB to track part history over time. The most well-known RFID protocols are ISO 14443 (A), ISO 15693, SO 18000. They differ in range and characteristics.
What are RFID tags?
There are different types of tags, in particular, universal or strictly for metal objects, in the form of stickers, tags, key chains, bracelets or labels. There are differences in devices depending on the memory used (one-time write, with the possibility of multiple reading, with the right to write other information).
There are active and passive tags. The former are able to work at a much greater distance, since they have their own power source.
Passive tags do not have an energy source. To clearly understand what type you need, you should consult the seller in the store.
The characteristics of the tag can be found in the product description.
Active tags can even transmit a signal through water or metal, and they can also be equipped with built-in sensors to assess temperature, humidity, light levels and other environmental parameters.
There is also such a variant of devices as semi-passive tags. They work on the same principle as passive ones, but are equipped with a battery to power the chip.
The tags also differ in price. For example, the cost of most passive devices rarely exceeds 20 US cents, but active tags can cost much more – 20-40 US cents. The cost depends not only on the type of device, but also on its properties, memory capacity and reliability of packaging.
RFID key, access control system
Contactless RFID cards are used as passes, transport cards or discount devices.
You can write down the necessary information on them and use them to identify employees who go to work through the checkpoint or to accumulate discounts in loyalty programs.
All information is stored on the card in complete security.
The cost of RFID cards is low. Many of them can be written to data repeatedly, not once. The operating frequency of RFID cards is 125 kHz. To start the reading process, it is enough to be at a distance of 5–70 cm. Information can be stored on such cards for an unlimited period of time. Cards have different standards (for example, closed MIFARE / MIFARE , and open CIPURSE).
RFID tags are a modern technology that helps to exchange information remotely, as well as record the necessary information on a microchip. Basically, the device is used to provide passage in the subway, marking goods and books in the library, and also as an additional function for smartphones.
In recent years, RFID has been used even more actively. In the future, the technology will be used in many areas of life, especially for access control and contactless payment. In industries such as pharmacology, they are already able to increase the level of protection against counterfeit medicines by implanting a device in every drug package.
